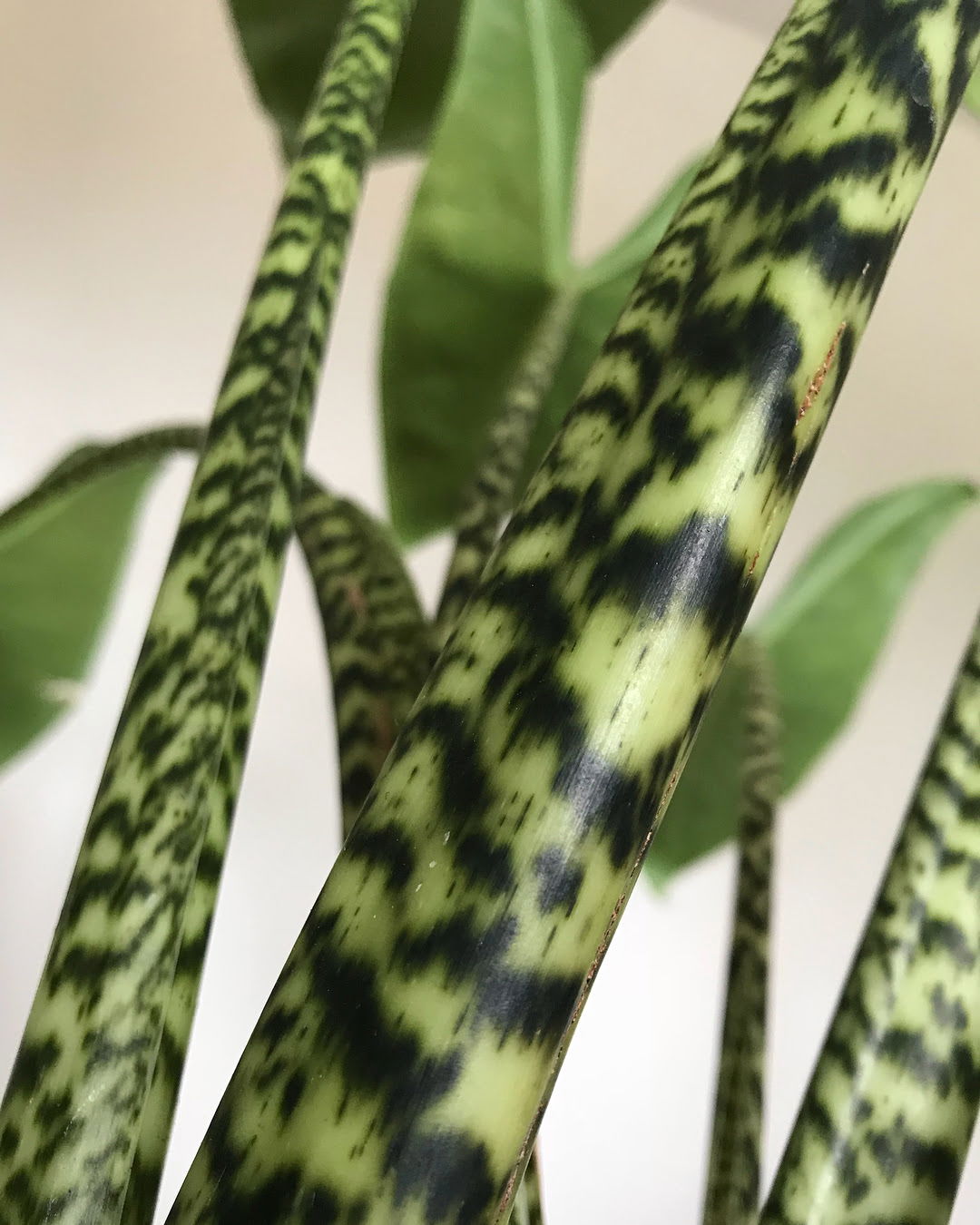

Alocasia zebrina
Contents
- Top Tips
- Location, Water, Humidity & Fertilisation
- Common Issues
- Origins, Temperature, Propagation, Repotting & Toxicity.
Need the answer to a specific plant query? Book a 1-to-1 video call with THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™, the website's friendly author, to overcome and address your niggling problem! Available on iMessage, WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger & more.
Top Tips & Info
- Care Difficulty - Easy to Moderate
- Alocasia zebrina grow best in spots that can provide near-perfect overhead lighting; within 2m of a window or in a semi-shaded conservatory are best for its overall health.
- Keep the soil evenly moist, allowing the top third to dry out in between waters. Avoid water-logging or extended periods of soggy-soil.
- Mist the foliage or introduce a humidity tray whilst the heaters are operating.
- Fertilise using a 'Houseplant' labelled feed every four waters in the spring and summer, reducing this to every six in the colder months.
- Keep an eye out for Spider Mites that'll form webs on the under-leaves of the plant.
- Especially if its kept in a dark location, wash or dust the foliage monthly, to increase the light-capturing efficiency.
- Repot every two or three years using 'Houseplant' labelled compost and the next sized pot. Scared about over-watering? Trade the plastic pot for terracotta so that the pot can absorb the excess moisture!
Location & Light - 🔸🔸
Although bright, indirect sun is ideal, throw in some morning or evening sun if possible. If it's situated in a shady location, dust the leaves from time to time to improve light-capturing efficiency. Never allow a Alocasia zebrina to sit in strong sunlight for extended periods, as too much light will result in a pale, washed-out appearance with possible brown patches forming on the leaves.
Most rooms in the house will easily accommodate a Zebra Plant, as long as there's a sufficient amount of light and space to grow. If the plant is situated in a darker location, be sure to wash the leaves monthly to improve its light-capturing efficiency and overall appearance. Do not situate a Alocasia in a setting that's prone to extreme heats or direct sunlight, for example, a south-facing conservatory, or within four metres of an operating radiator.
Water - 🔸🔸
Allow third of the soil to dry out in between irrigations, while reducing this further in the autumn and winter months. For those grown in brighter locations, only allow a third of the soil dry out to minimise the chances of dehydration. Under-watering symptoms include stunted growth, brown leaf edges and yellowing leaves. Over-watering symptoms include a collapsed stem, yellowing leaves and plant death. If you feel over-watering is to blame, remove the affected leaves, roots and soil and replace with a fresh batch of houseplant compost. Click on this link for more info about addressing root rot.
Humidity - 🔸🔸🔸
Alocasia zebrina originate from the Philippines, meaning high humidity is mandatory for quality growth. Mist both sides of the leaves once a week in summer and twice in winter; browning leaf-tips are a big sign that the surrounding air moisture is too low. A quick hose down once a month will hydrate the leaves, eliminate dust particles and help reduce numbers of pests, most notably Spider Mites.
Fertilisation - 🔸🔸
Feed every four waters during the growing period and every six in the autumn and winter, using a 'Houseplant' labelled fertiliser. Never apply a 'Ready to Use’ product into the soil without a pre-water first, as it may burn the roots and lead to yellowed leaves.
Common Issues with Alocasia Zebrina
An array of simultaneous cultivation issues will increase the chance of developing yellowed leaf-sections with browned halos - see image below for visual reference. Firstly, the location may be too dark, with its compost staying too saturated in-between waters; if mould is growing across the soil, this is usually a bad sign. Further, you're potentially using too cold water or tap water that hasn't been allowed to sit for 24hrs. The final culprit might be lack of fertilisation, with regular feeds being paramount for long-lasting, healthy leaves. If the specimen hasn't been nourished in over two months, it'll begin to show signs of nutrient deficiencies seen in this article.
If this common problem has occurred with your specimen, remove the affected leaves (not areas) and improve the growing conditions considerably. Fertilise regularly with lukewarm water and be sure to allow the top third to dry out in between hydrations.
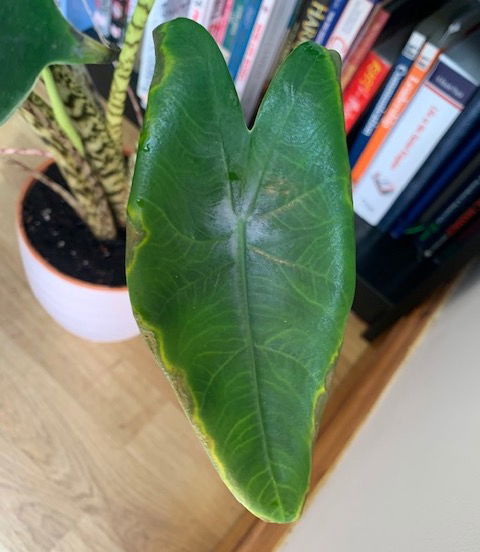 The most common issue among Zebra Plant owners. Example 1.
The most common issue among Zebra Plant owners. Example 1.
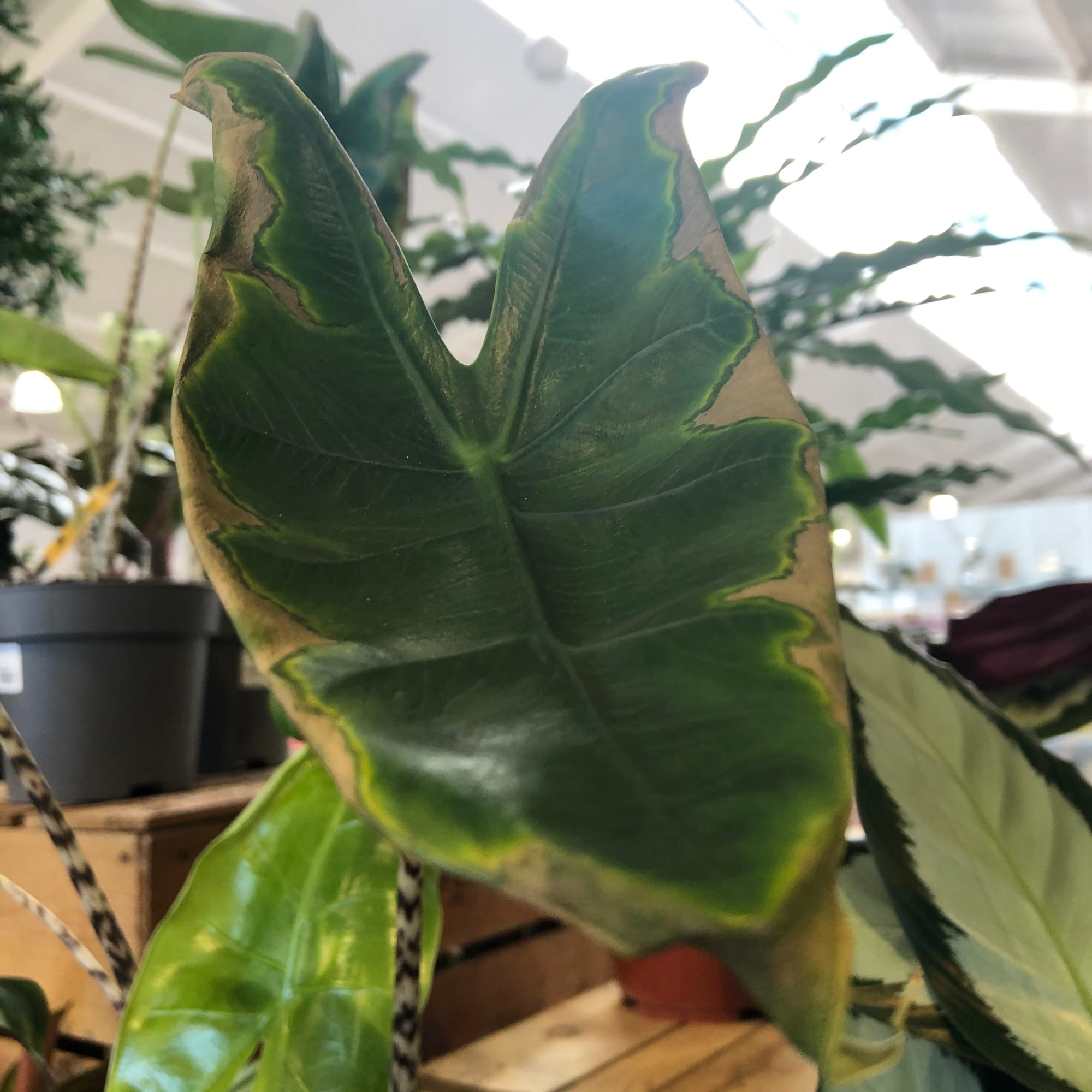 Example 2.
Example 2.
Regular irrigations are key. Periods of droughts will quickly slip the specimen back into its dormancy period, causing stunted growth and a bewildered plant owner. If it hasn't repotted in a while, there may be too many roots and not enough soil to retain moisture, thus leaving the soil to dry out quicker. Click on this link to learn more about a transplant.
Pests could arise at any time, with infestations starting from the original nursery or via contamination in your home. Spider Mites and Mealybugs tend to be the usual inhabitants, with the first being minute and almost transparent, roaming the leaves in search of chlorophyll and a site to hide its eggs. The latter, however, will stand out much more, with white cottony webs developing across the foliage and stems. Thoroughly check the plant's cubbyholes before giving it the all-clear, or click on the appropriate links to learn more about eradicating these issues.
 Alocasia can be riddled with pests due to its thin, broad leaves. In the image above, there's a third point of interest to look at - mineral/calcium deposits. This is a natural part of an Alocasia leaf's lifecycle, so don't worry about removing them!
Alocasia can be riddled with pests due to its thin, broad leaves. In the image above, there's a third point of interest to look at - mineral/calcium deposits. This is a natural part of an Alocasia leaf's lifecycle, so don't worry about removing them!
Yellowing lower leaves (closest to soil) are a clear sign of over-watering, usually caused by too little light. Although Alocasia zebrina can do well in darker locations, the frequency of irrigations must be reduced to counteract the chance of root rot. People don't realise that a plant's root system needs access to oxygen too; when soil is watered, the air will travel upwards and out of the potting mix. A lack of accessible oxygen for the roots will cause them to subsequently breakdown over the oncoming days. Click on this link to learn more about root rot and how to address it, and always feel the pot's weight for confirmation (heaviness = good soil moisture, & vice versa).
Too low humidity can cause browning leaf tips with yellow halos. Although this won't kill your specimen, you may want to increase the local moisture to prevent the new growth from adopting these symptoms. Mist or rinse the foliage from time to time and create a humidity tray whilst the heaters are active to create a stable environment for your specimen.
Snapped stems are common with Alocasia zebrina that are grown too low light. Increase the light levels by placing it as close to a sunless windowsill as possible. If it's too big for a windowsill, try placing it directly in front to help the plant grow stronger, more upright stems. You can either try strengthening the damaged stem by using a chopstick as support or simply prune it entirely off.
Dust the leaves regularly. Although this isn't too much of an issue, a build-up of dust particles can clog up the plant's pores, causing lowered light capturing-efficiency. Wipe the topsides of the leaves down once a month to keep levels down and improve growing conditions.
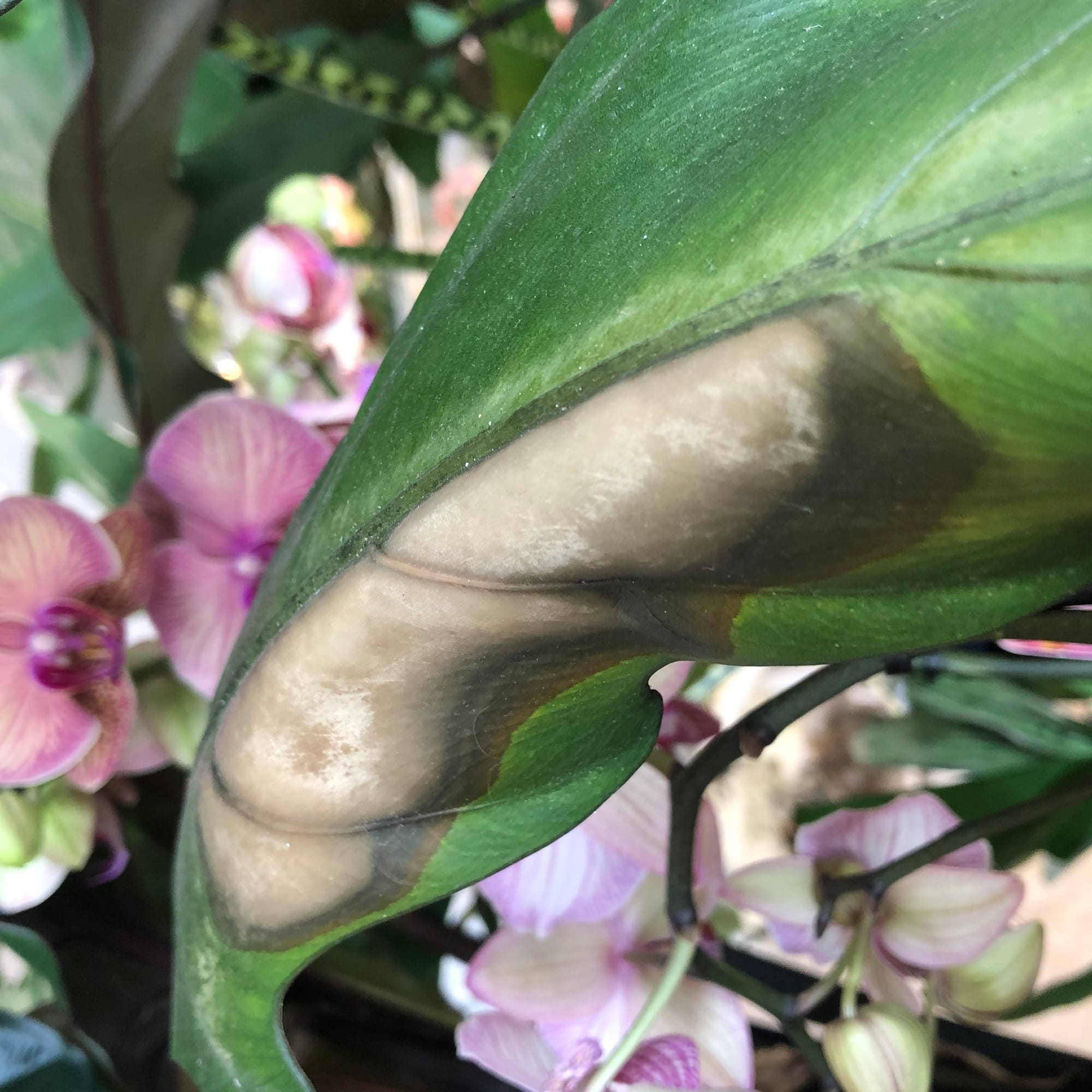 Sun Scorch is another issue that may face an Alocasia zebrina if exposed to too much sunlight. Click on the image to learn more about addressing this problem.
Sun Scorch is another issue that may face an Alocasia zebrina if exposed to too much sunlight. Click on the image to learn more about addressing this problem.
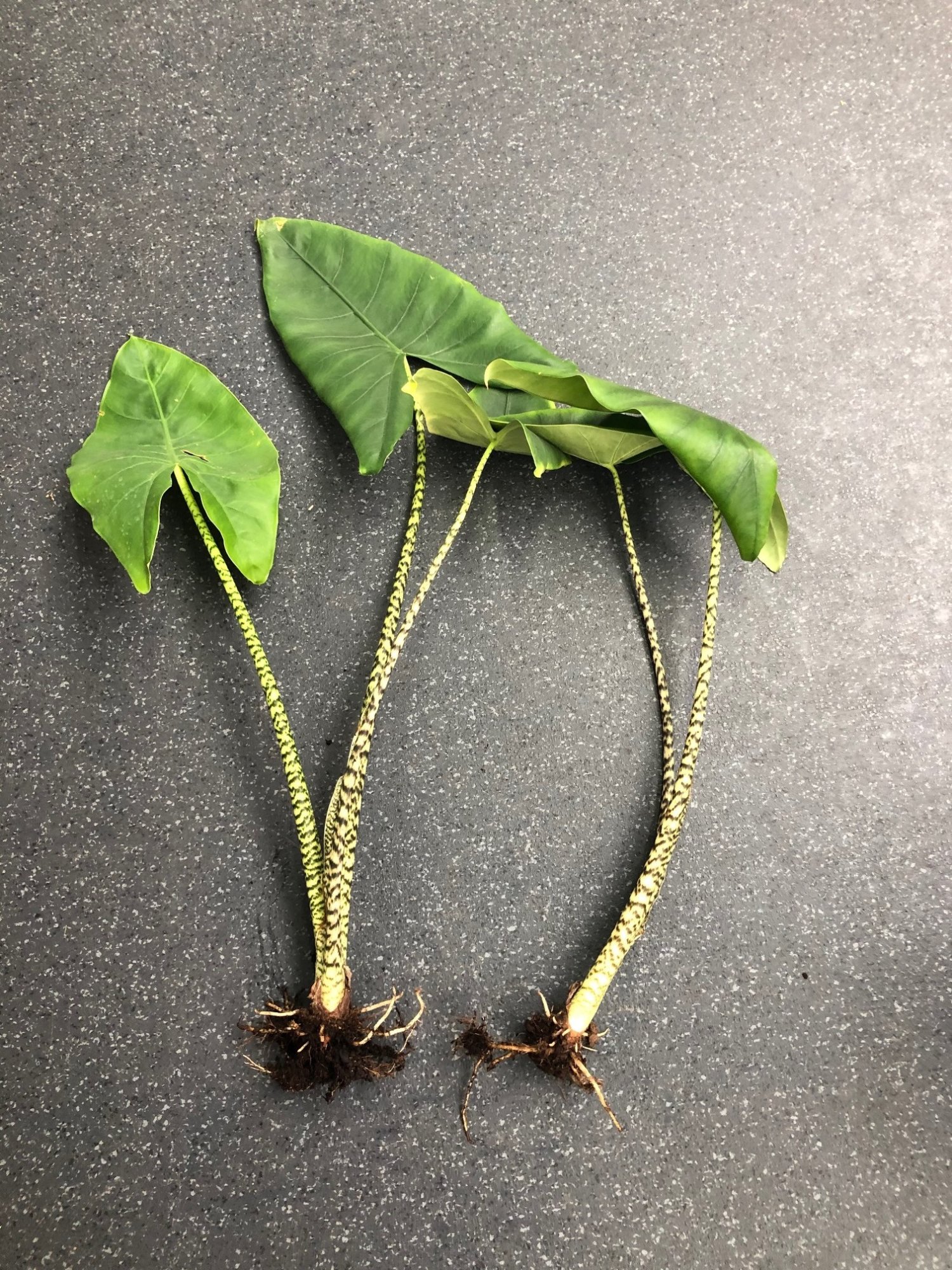
Small lumpy growths on the root system are nothing to worry about; they are actually what's known as 'cormlets' that can be propagated to make its very own Zebrina! Scroll down to 'Propagation' to learn more.
If your Alocasia begins to wilt, it could be the product of one or many issues, ranging from the environment to your care habits. If the specimen is located in too low light, it may lead to plant-confusion when the window is several metres away. As mentioned in 'Location & Light', most Alocasia will require overhead lighting to complement its growth habit, with anything else causing either wilting or slanted growth. Secondly, irregular watering habits could cause root dehydration, which will eventually lead to wilting. Prolonged droughts will result in a lack of hydration in the upper part of the plant, with root rot doing the same - albeit it with overly soggy compost. Finally, environment shock could be the final culprit of your wilting Alocasia. If the specimen has recently been purchased or relocated, the chances are that the specimen hasn't acclimated itself to the new environment. Be sure to provide a bright, indirect setting with the best possible angle to the light source (overhead or nearby a window). Maintain relatively moist soil, allowing the top third to dry between waters and fertilise every two to four weeks, depending on the current season. If you still have questions about your poorly Alocasia, be sure to book a 1-to-1 Call with THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™ to discuss this further!
Mould developing on the soil means two things - too little light and over-watering. Despite the harmlessness of the mould, it'll prove unsightly to most gardeners and is therefore removed once known. To remove, replace the top two inches of the soil for a fresh batch of 'Houseplant' compost. Either increase the amount of light received (no direct sunlight for the first few weeks to prevent environmental shock) or decrease the frequency of waters slightly. If the mould is accompanied by yellowing lower leaves, you may also have a case of root rot.
There are several species of Leaf-Spot Disease, (Graphiola, Botrytis, Anthracnose & Cercospora) and all of them operate in the same way. Fungi spores will land on the leaf's surface and will slowly develop along with the plant. Unfortunately, as there aren't any products that'll address the issue head-on, you can only remove the affected areas and regularly wash the leaves to limit the spread. In some cases, however, the small yellow spots are caused by inconsistent soil moisture, and is not the direct product of a disease. Think about your own cultivation habits and make a decision of what to do.
 Root rot is a key issue with owners, especially those kept in cold or dark locations. The base of a Zebra Plant has a corm, which acts similarly to a bulb so short-lived droughts can be survivable; always considered this when potentially over-watering your specimen.
Root rot is a key issue with owners, especially those kept in cold or dark locations. The base of a Zebra Plant has a corm, which acts similarly to a bulb so short-lived droughts can be survivable; always considered this when potentially over-watering your specimen.
Origins
The Alocasia zebrina were first discovered by Heinrich Schott in the early-mid 1800s in the Philippines. Despite its high levels of calcium oxalate chrystals which can cause temporary speechlessness, if the corm is cooked long enough it's safe to eat, providing high levels of starch that can be used as energy or stored in the body.
 The Distribution of Alocasia zebrina.
The Distribution of Alocasia zebrina.
Temperature
12° - 30°C (54° - 86°F)
H1b (Hardiness Zone 12) - can be grown outdoors during the summer in a sheltered location with temperatures above 12℃ (54℉), but is fine to remain indoors, too. If you decide to bring this plant outdoors, don't allow it to endure more than an hour of direct sunlight a day as it may result in sun-scorch. Regularly keep an eye out for pests, especially when re-introducing it back indoors.
Spread
Up to 2m in height and 1m in width, with the ultimate height being reached in around 5 - 10 years indoors. Alocasia zebrina are best grown with overhead lighting to compliment their growth structure; locations with lateral light sources (e.g. the corner of a room) will cause stunted, lopsided growth - so it's best to keep them in conservatories or close to windows!
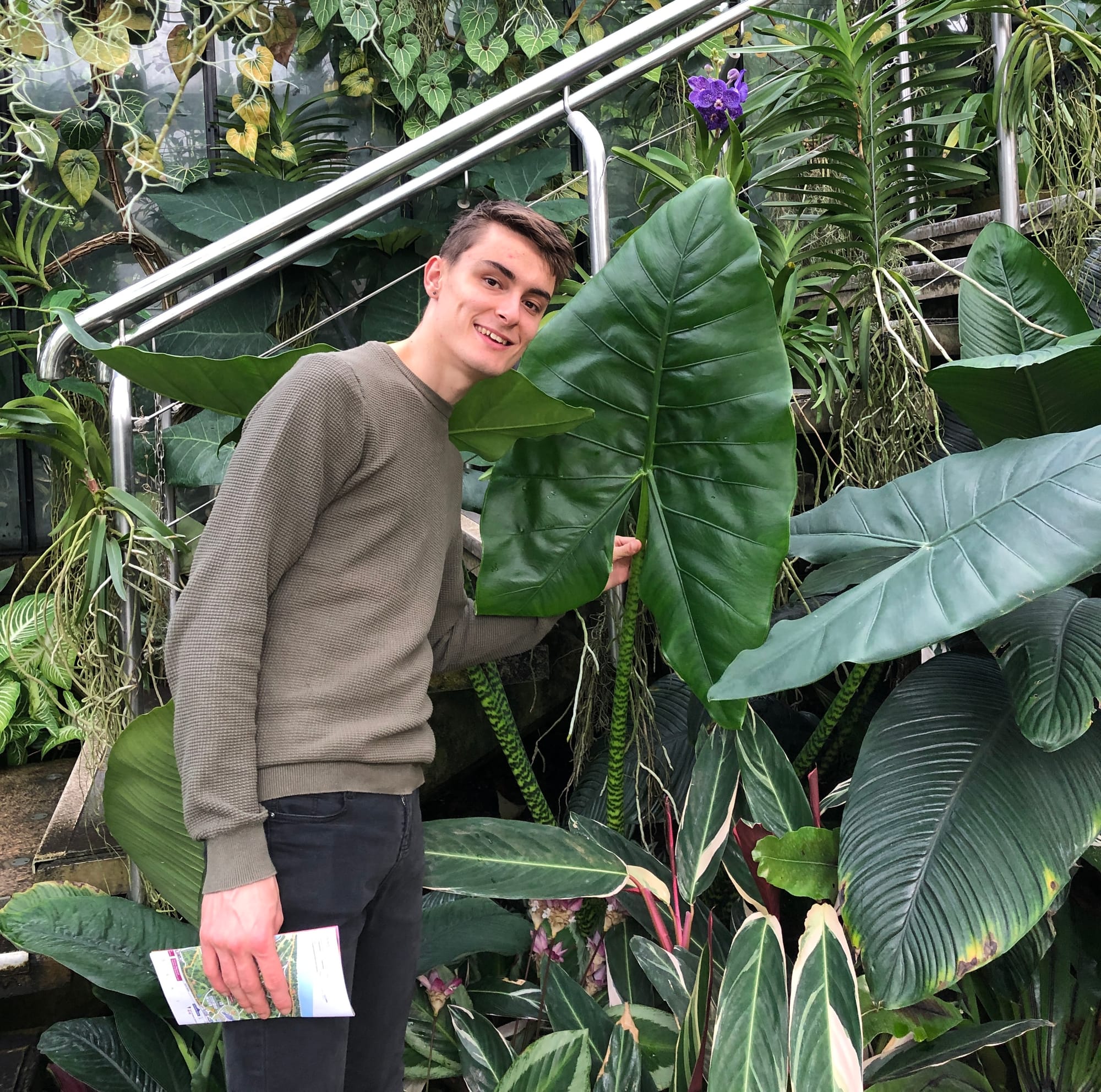 Here's Joe Bagley, THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™, with a mature Alocasia zebrina at Kew Gardens, UK. The size of its leaf is still relatively small compared to those that grow in the wild!
Here's Joe Bagley, THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™, with a mature Alocasia zebrina at Kew Gardens, UK. The size of its leaf is still relatively small compared to those that grow in the wild!
Pruning
Remove yellow or dying leaves, and plant debris to encourage better-growing conditions. While pruning, always use clean scissors or shears to reduce the chance of bacterial and fungal diseases. Never cut through yellowed tissue as this may cause further damage in the likes of diseases or bacterial infections. Remember to make clean incisions as too-damaged wounds may shock the plant, causing weakened growth and a decline in health.
Propagation
Via Seed or Corm Propagation
Seeds (Difficult) - This form of propagation isn't common due to the difficulties growers might face trying to source seeds. For those who have the seeds ready, submerge the Alocasia seeds around 1cm deep in an 'Alocasia' labelled potting mix in a seed tray. Maintain reliable soil moisture and provide a bright, sunless windowsill while they germinate. You can separate the seedlings into individual 5cm pots once they produce their third leaf.
Corms (Easy to Moderate) - Most Alocasia are have corms, which are small globular-shaped brown bulbs that'll grow along the root system. A mature Alocasia Zebrina can produce over ten corms at any time and can be harvested when you next repot it. Here's how to do it;
- The best time to repot is during the spring or early summer. Make sure that a few hours before repotting, you water the plant's soil to reduce the risk of 'transplant shock' when the roots are disturbed in dry soil.
- Take the mother plant out of its pot and gently work your fingers through the rootball (& soil) until you feel the small brown ball-shaped 1-2cm corms. Have a look at the image below for what they look like!
- With a clean pair of scissors or a knife, cut off the corm via the 'rhizome' (root) that attaches it to the mother's root system. Make sure around 0.5cm+ of the 'rhizome' is still attached to the corm, so don't prune too close to the bulb itself. Have a look at the images below.
- Once separated, place the corm sideways in a small glass (like a shot glass) or plastic cup. Pour around 20ml of water, so it creates a small puddle of water which should submerge around 10% of the corm. Do not fully submerge the corm as this could result in it rotting. Place the corm (in its container) in a warm, bright windowsill until roots develop which will take between 2-8 weeks. Replace the water twice a week to remove any bacteria. See the image below!
- One the roots are around 3cm (1in) in length (pictured below), plant it in fresh 'Alocasia' labelled potting mix in a 5-7cm plastic pot.
- With the mother plant, repot her back into its orignal pot with a fresh batch of 'Alocasia' labelled potting mix. If you're growing the mother Alocasia in hydroponics, repot this back into the same pot with fresh potting medium.
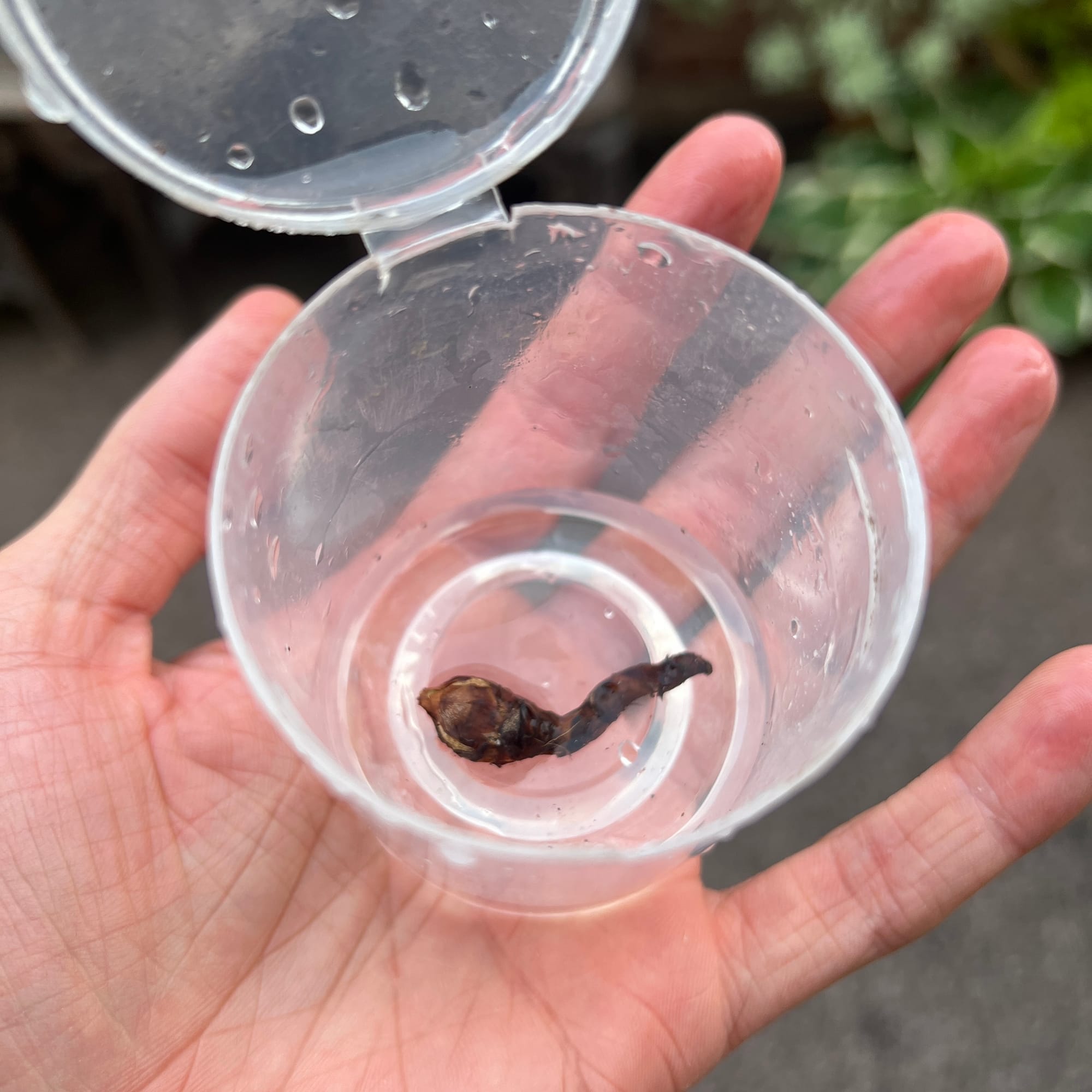

This is how you 'puddle' an Alocasia corm by submerging it in water to root. Never submerge the entire corm in water as this increases the likelihood of it rotting.
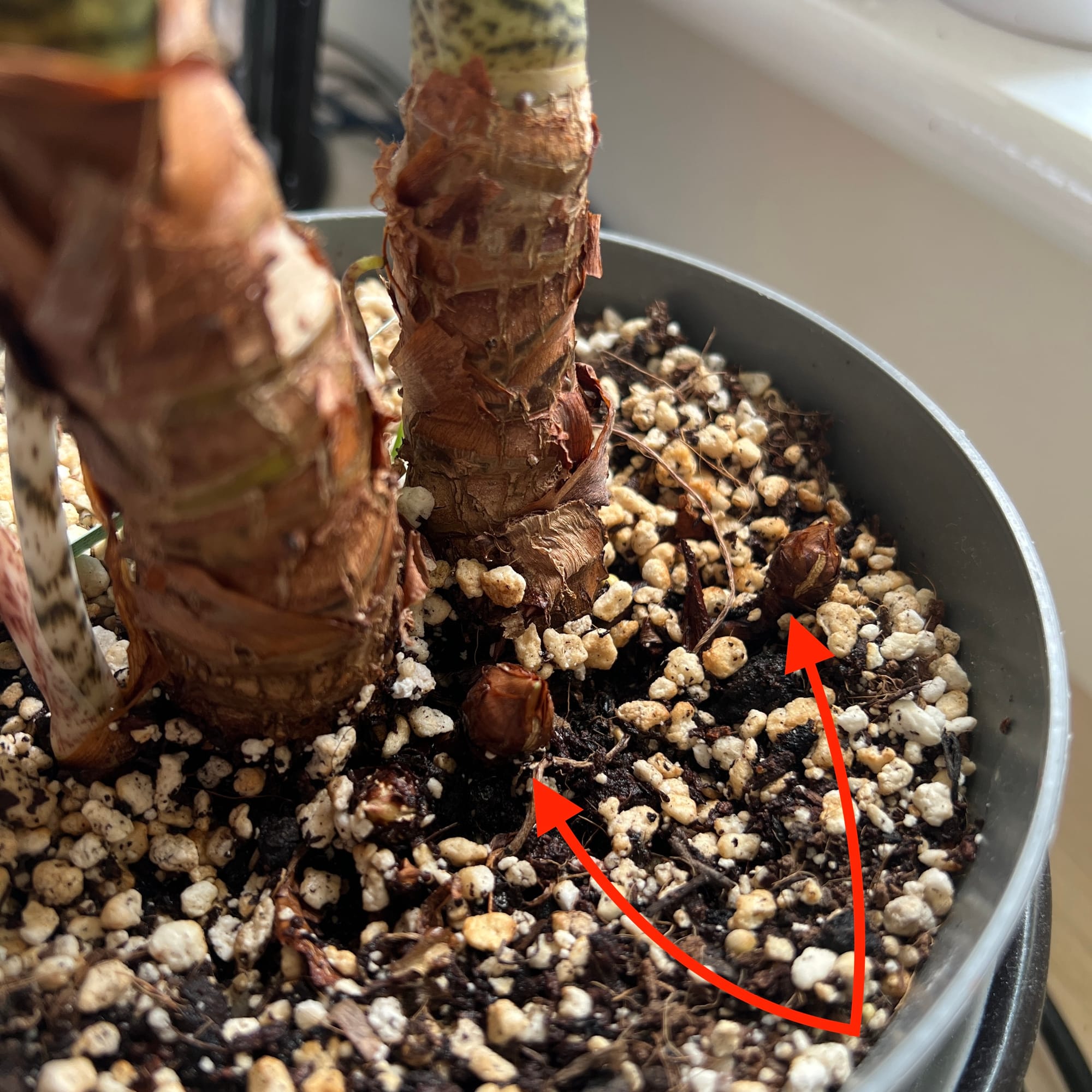

Where do you find an Alocasia zebrina's corms?
You can find the corms either within the soil or on top (like the image above!).
 Extra Tip: A healthy corm should be solid when pinched. Discard any bulbs that are softened or rotten as the bacteria will kill the whole corm.
Extra Tip: A healthy corm should be solid when pinched. Discard any bulbs that are softened or rotten as the bacteria will kill the whole corm.
 Here's a corm that THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™ has grown hydroponically and is now ready to be planted in either soil or moss. (He recommends Sphagnum Moss as a good growing medium).
Here's a corm that THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™ has grown hydroponically and is now ready to be planted in either soil or moss. (He recommends Sphagnum Moss as a good growing medium).
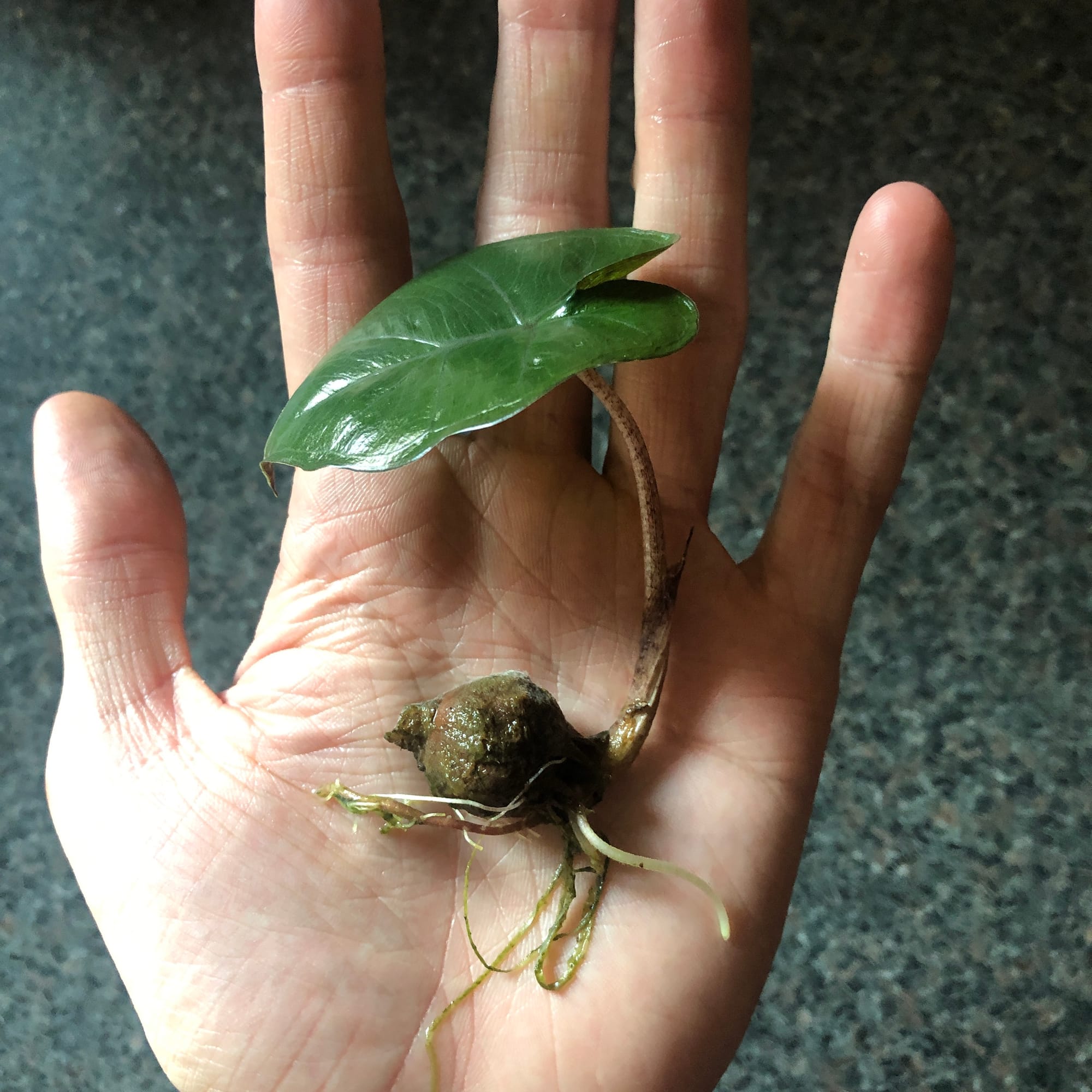 A fantastic example of a Zebrina cormlet that's produced roots and a leaf from being propagated with the advice mentioned above! Note: A healthy corm should be brown & hard when pinched; discard any soft or rotten bulbs as they pose a threat of bacteria in the potting mix.
A fantastic example of a Zebrina cormlet that's produced roots and a leaf from being propagated with the advice mentioned above! Note: A healthy corm should be brown & hard when pinched; discard any soft or rotten bulbs as they pose a threat of bacteria in the potting mix.
Flowers
As Alocasia is part of the Araceae family, their flowers aren't showy. Much like a Peace Lily's flower body, their flowers consist of a white or green spathe (the spoon-like shell) with the spadix being the site of pollination. Blooms can last up to five days and is usually visible during late spring or early summer around 30cm+ from the soil line.
Repotting
Repot every three years in the spring, using a 'Houseplant' labelled soil or our very own Alocasia Potting Mix and the next sized pot with adequate drainage (we recommend terracotta). Hydrate the plant 24hrs before tinkering with the roots to prevent the risk of transplant shock. Gently check around the root system for small lumpy growths (called 'corms') which can be propagated separately to make even more Zebrina plants (see image above). Click here for a detailed step-by-step guide on transplantation, or via this link to learn about repotting with root rot.
Pests & Diseases
Keep an eye out for mealybugs, spider mites, scale & thrips that'll locate themselves in the cubbyholes and undersides of the leaves. Common diseases associated with Alocasia are root rot, red leaf-spot, botrytis, powdery mildew & southern blight - click here to learn more about these issues.
Toxicity
Members of the Araceæ family typically contain poisonous calcium oxalate crystals, with Alocasia being no exception. Other members of this family include Philodendron, Zamioculcas (ZZ Plants) and Spathiphyllum (Peace Lilies). If eaten, vomiting, nausea with a loss of appetite could occur and consumption of large quantities must be dealt with quickly.
Retail Locations
Online Stores.
Book a 1-to-1 Call with THE HOUSEPLANT DOCTOR™
If you need further advice with your houseplants, book an advice call with ukhouseplants' friendly and expert writer today! This can be done via a video or audio call on most apps, including Facebook, FaceTime & Skype. A ten-minute call costs £5.99 (US$7), or £15.99 for thirty minutes. You can ask multiple questions, including queries on plants, pests, terrariums, repotting advice and anything in between. Please consider supporting this service to keep ukhouseplants thriving!